FL-MiniLLM
Federated knowledge distillation of generative LLMs
Background
Federated learning (FL) is a powerful machine learning technique that allows model training to occur across multiple decentralized devices concurrently to train a strong ML model, where the client private data never leaves the device and only the model parameters are shared with the server.
At the same time, with the rise of ChatGPT everyone can appreciate the power of Large Language Models. The enormous amounts of text data generated by users every day can be potentially used to empower the training of LLMs, but this normally raises privacy concerns. Thus, FL would allow us to gain the benefits of training on client data without compromising their privacy.
Existing Solutions
FedAvg
FedAvg is one of the most widely used FL frameworks. During each communication round, the clients will each perform training locally with their private data, and then share their model weights to the server. The server aggregates the model weights by averaging and returns the new aggregated model to the clients. The problem is that FedAvg (and other parameter averaging FL schemes) require the client models and the server model to all have the same architecture, which is impractical in cases where LLMs can have up to billions of parameters and use >10GBs of memory just to run.
Federated Knowledge Distillation
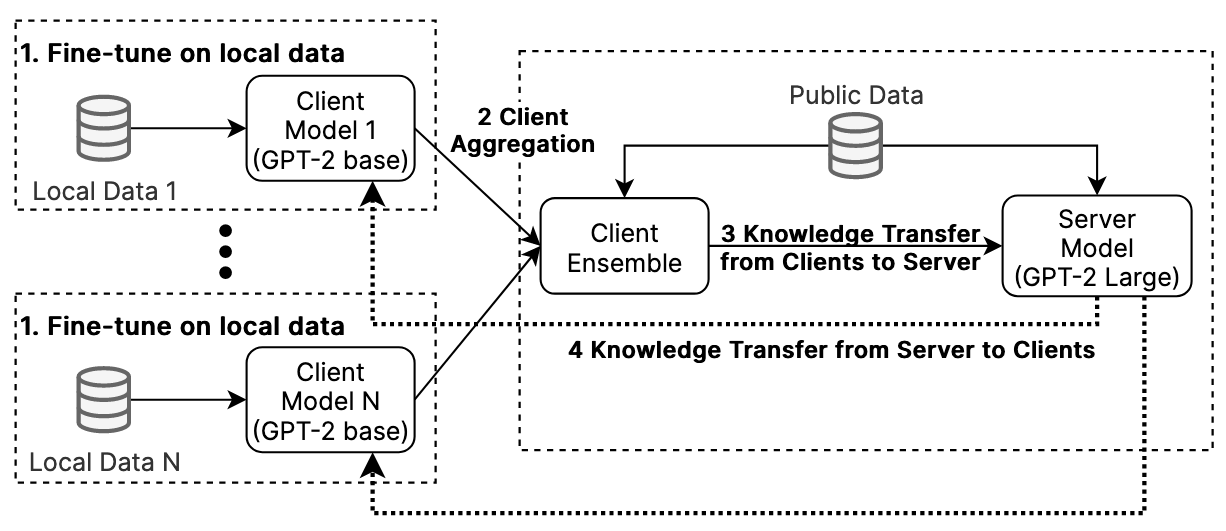
Federated Knowledge Distillation (KD) frameworks address this by incorporating knowledge distillation between models instead of parameter averaging, which allows heterogeneous model architectures between the server and the clients. However, existing Federated KD frameworks are only applicable for classification tasks like sentiment analysis, but we all know the true power of LLMs come from being able to generate sequences.
Our Solution
We therefore devised a Federated Learning framework that works using sequence-level knowledge distillation. At each communication round, the clients and the server alternatively switch roles as the teacher and the student. The teacher generates language sequences according to the input, and the student uses a PPO (Proximal Policy Optimization) approach and minimizes the reverse KL-Divergence to the teacher distribution.